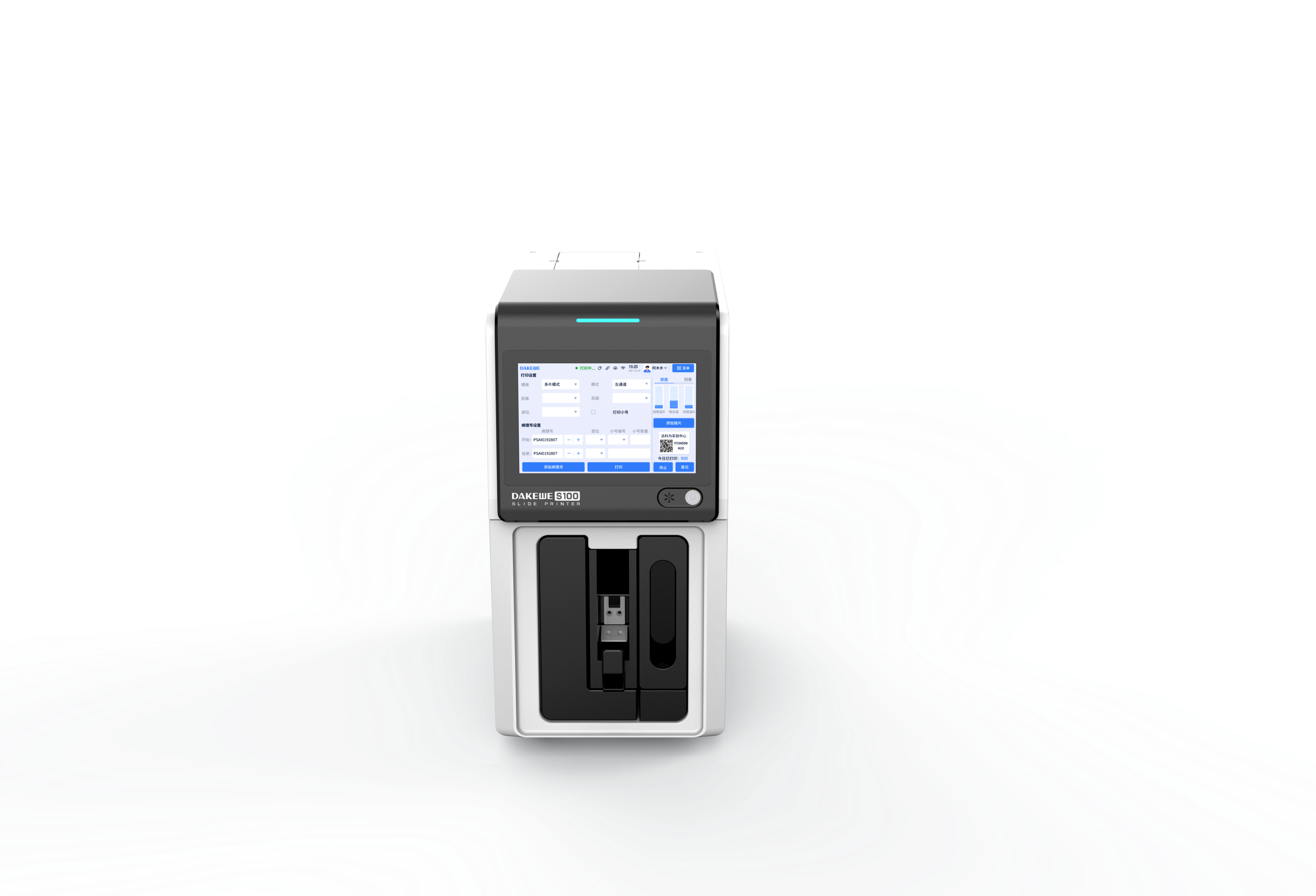
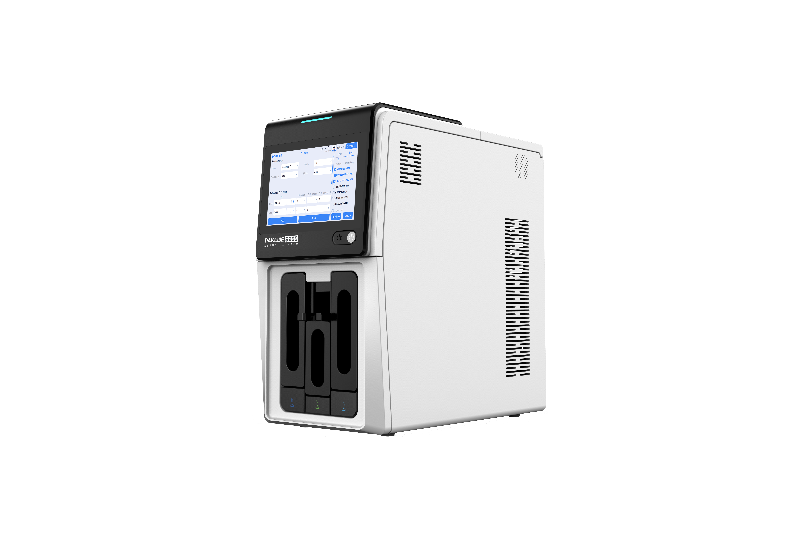
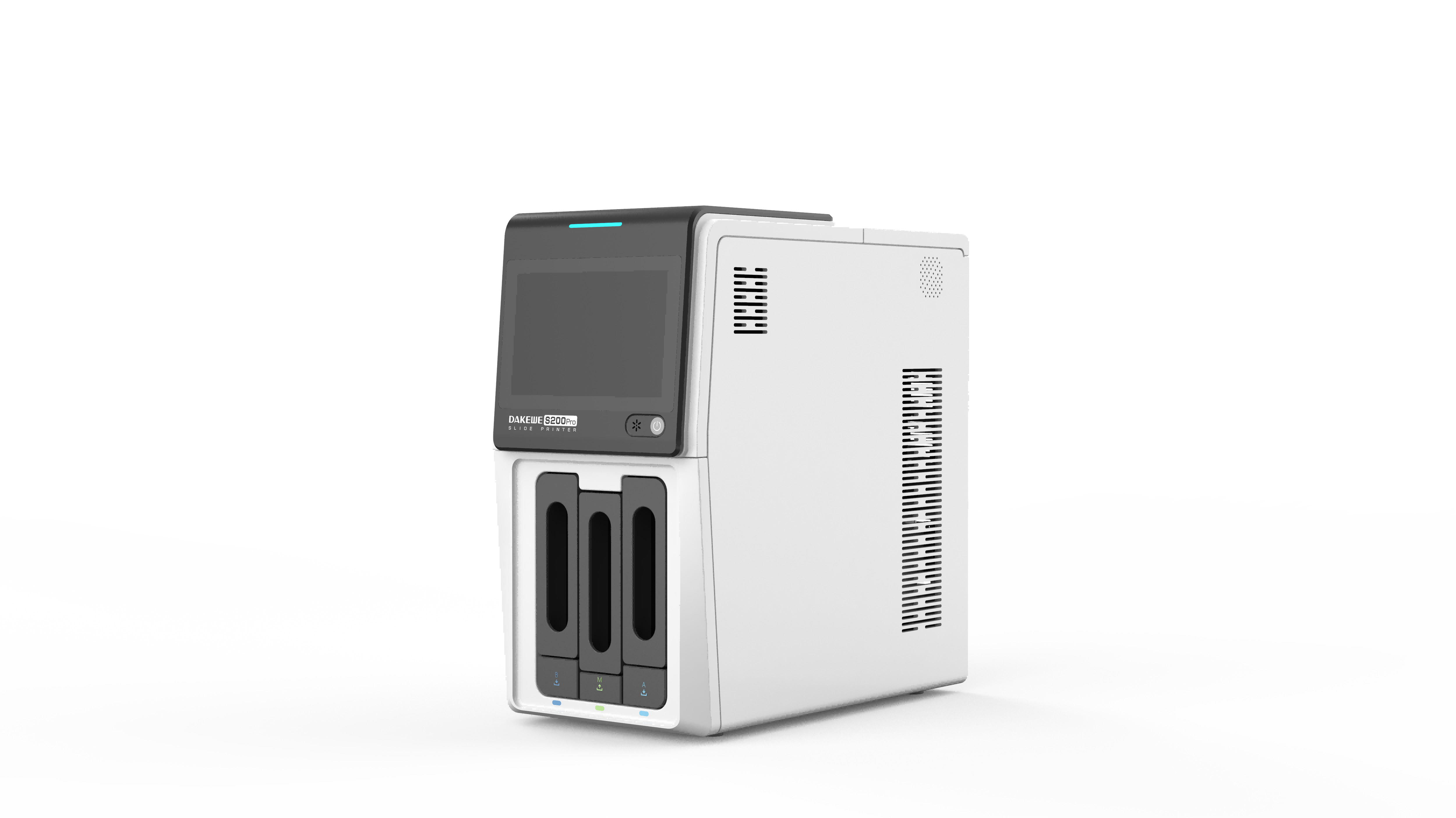
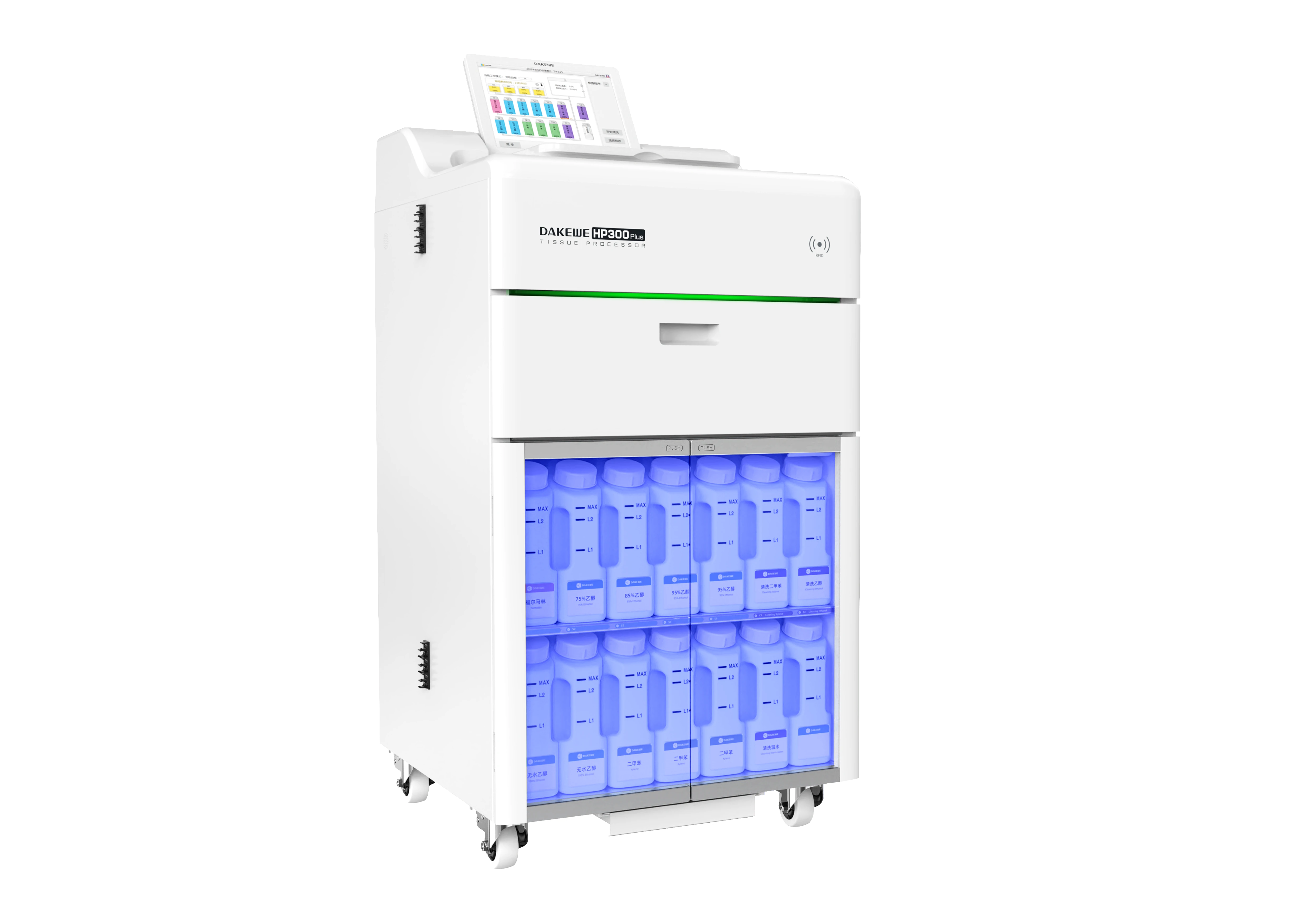
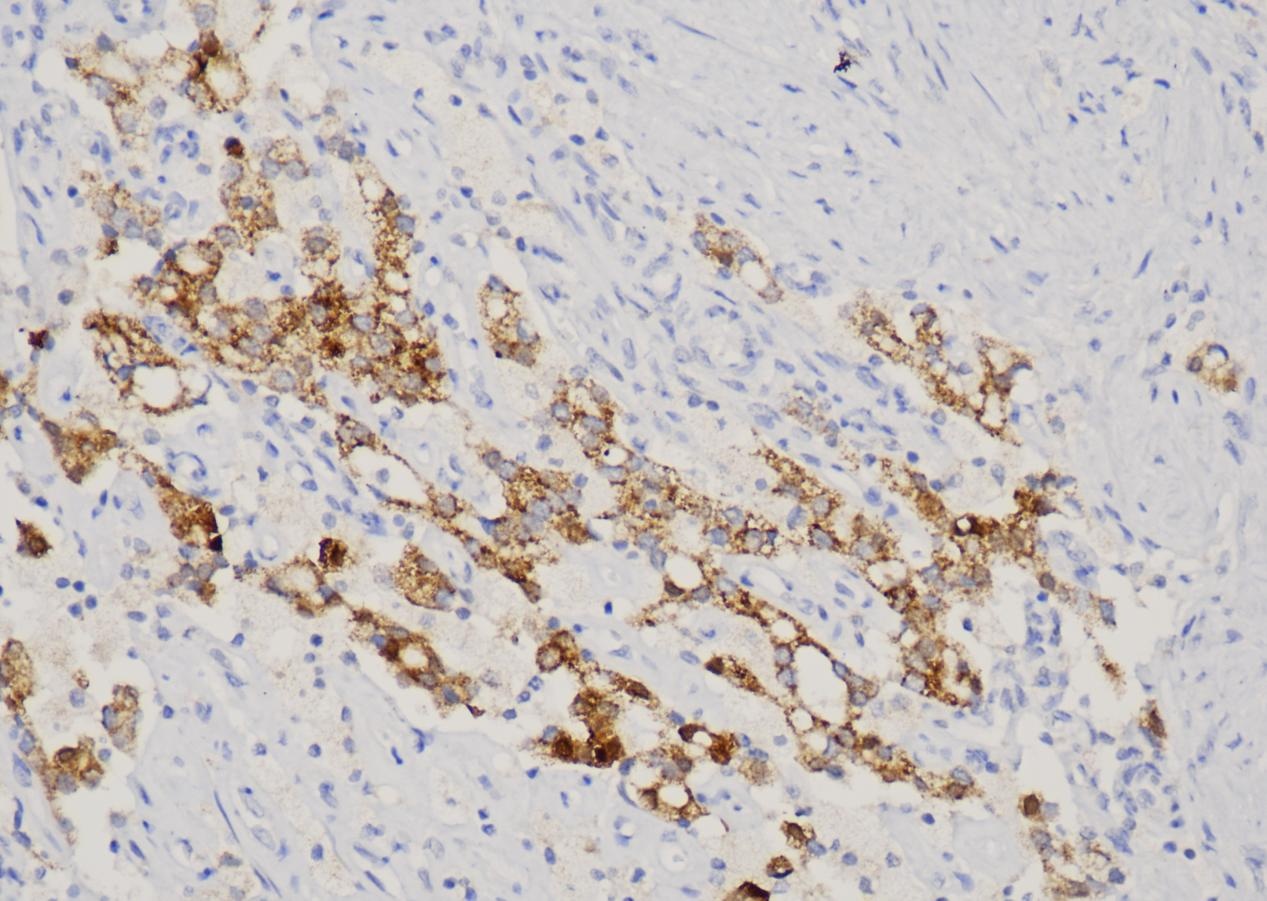
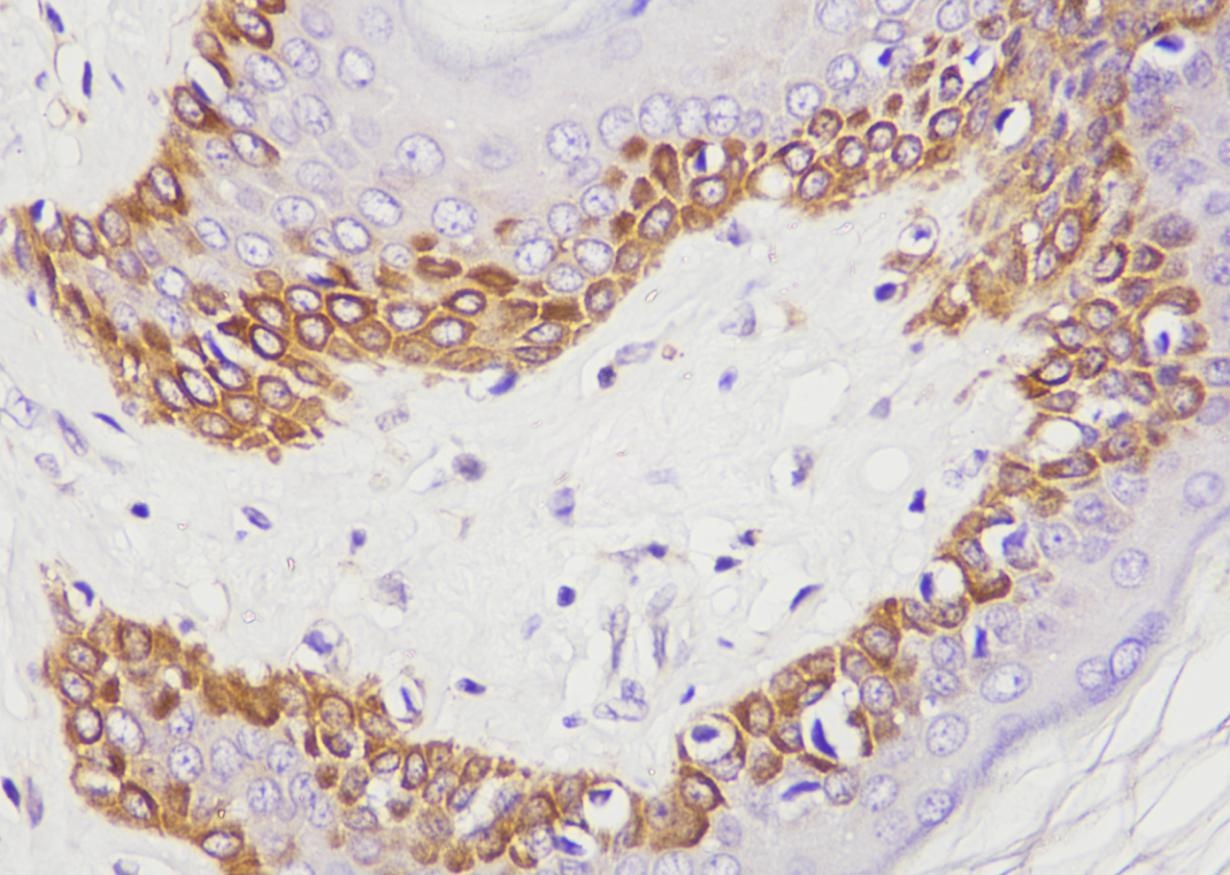
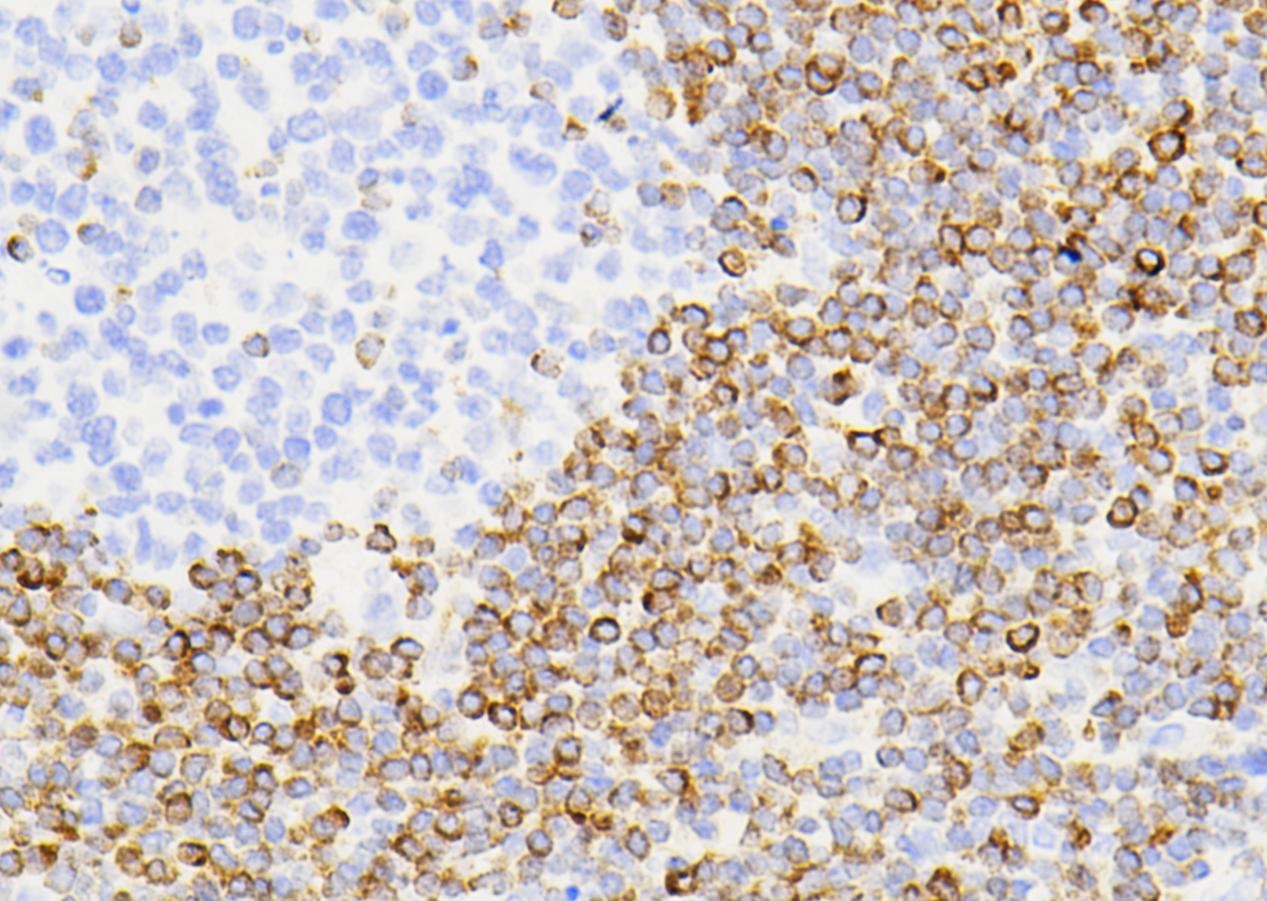
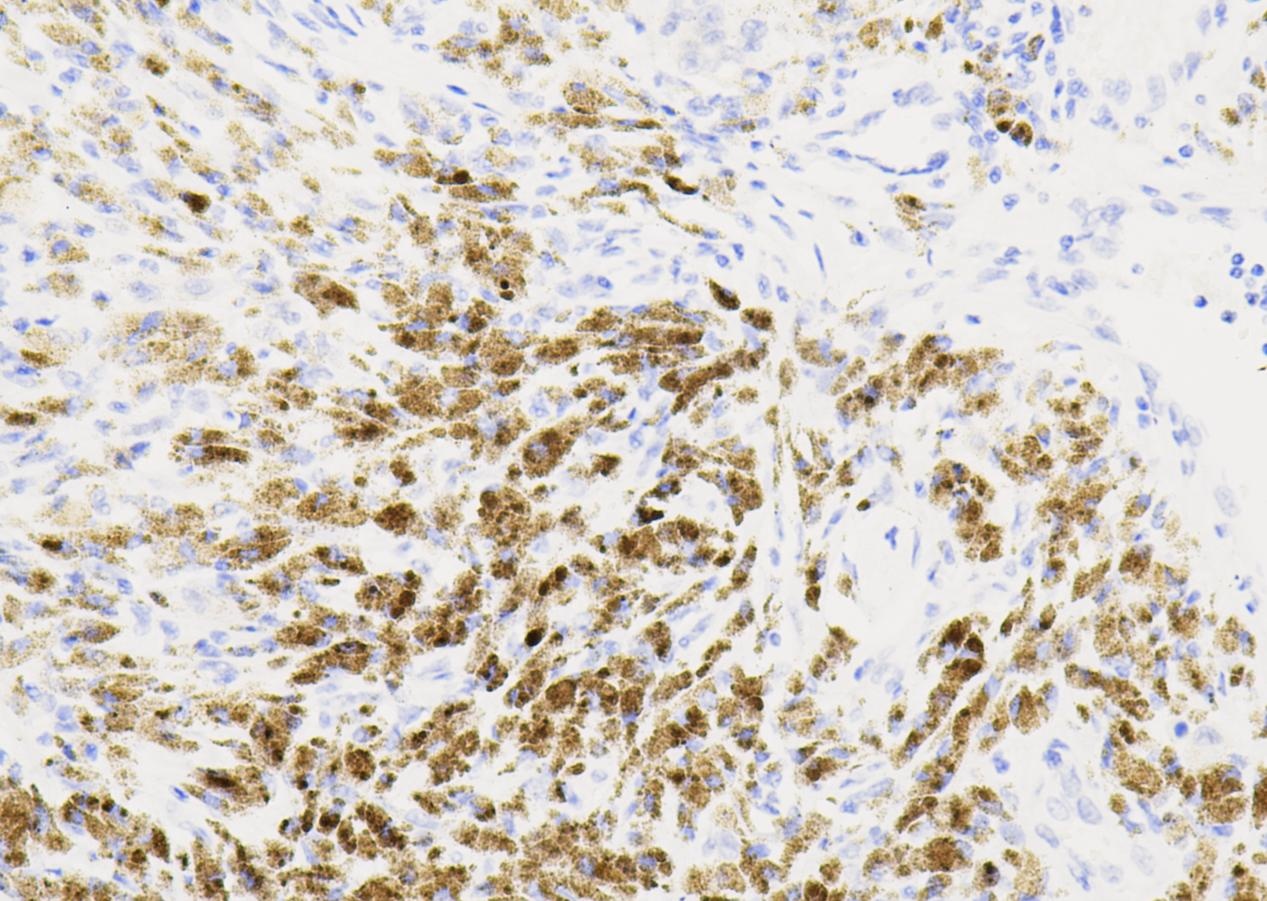
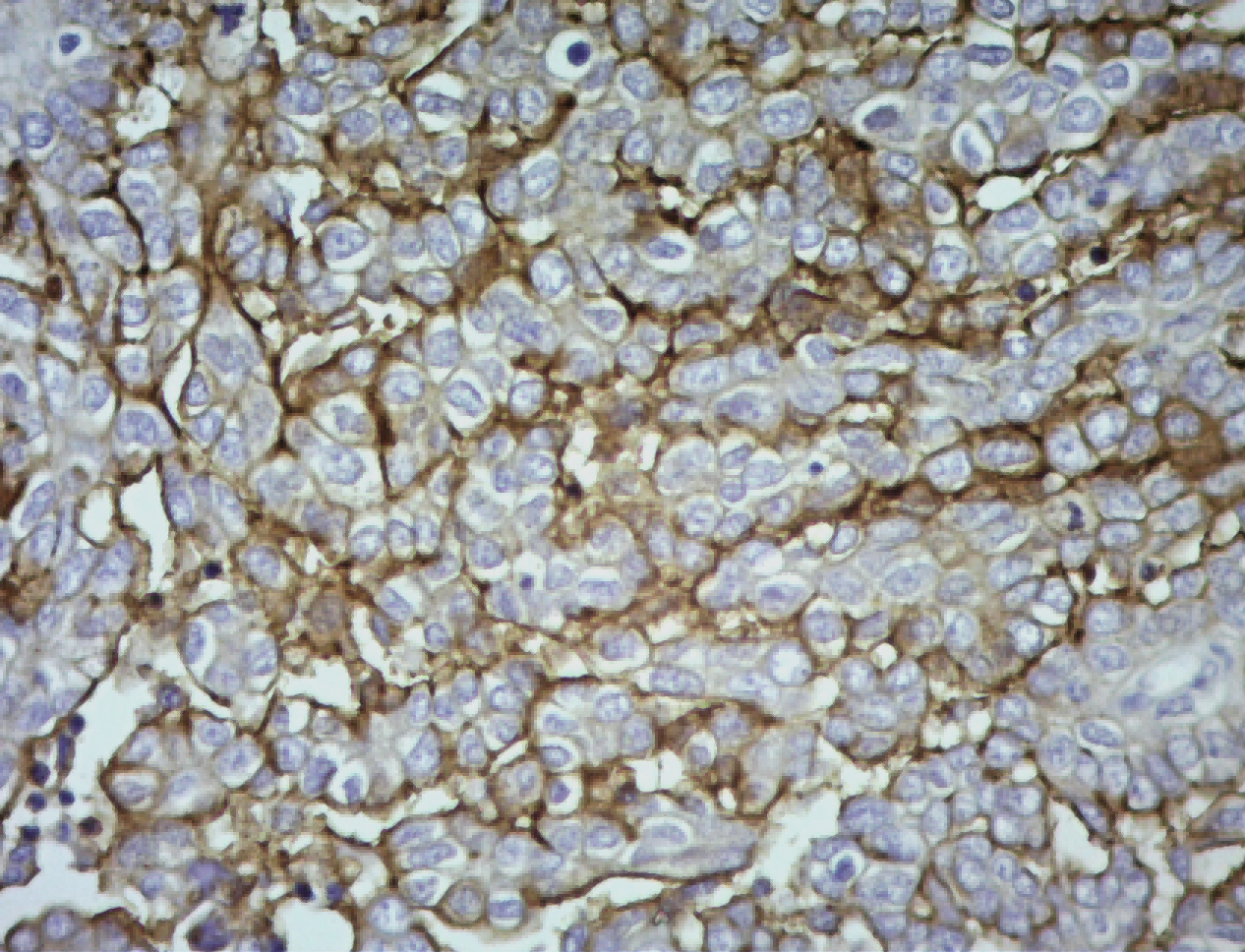
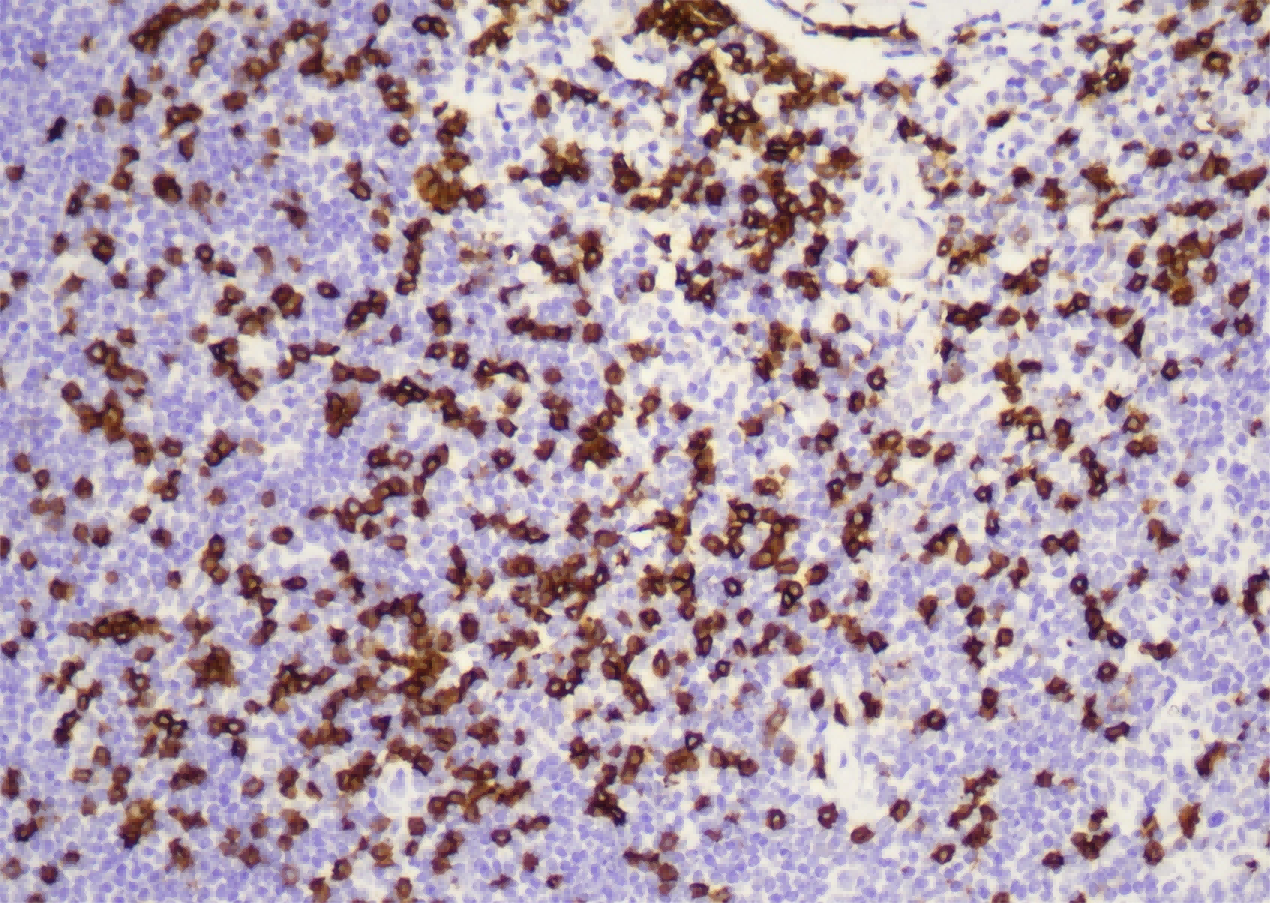
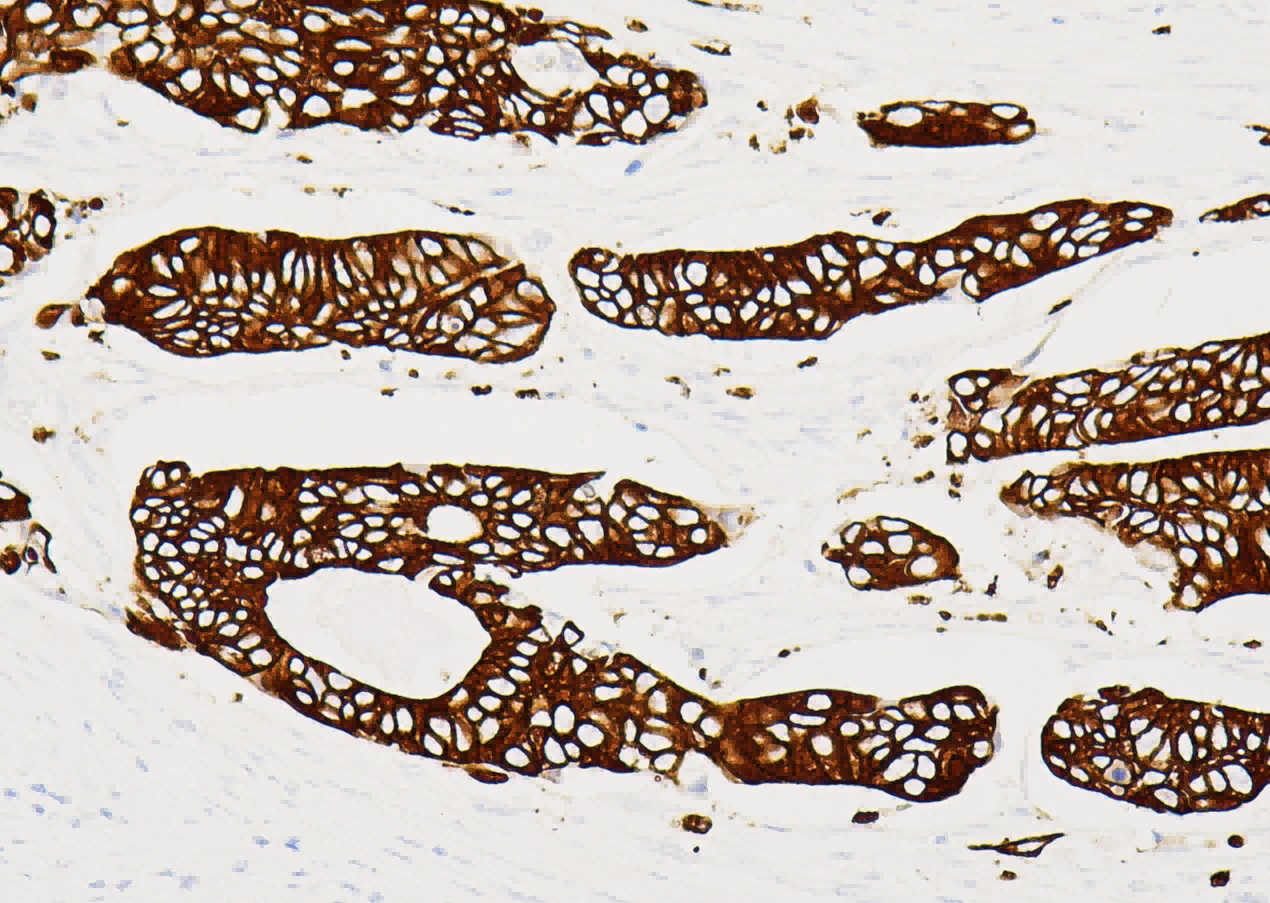
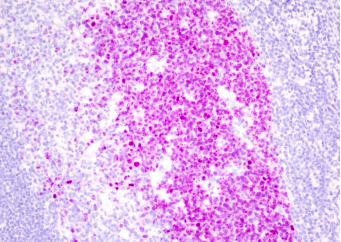
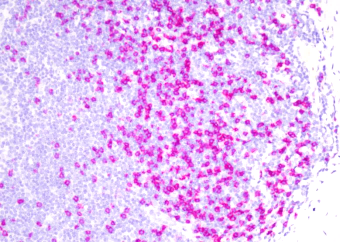
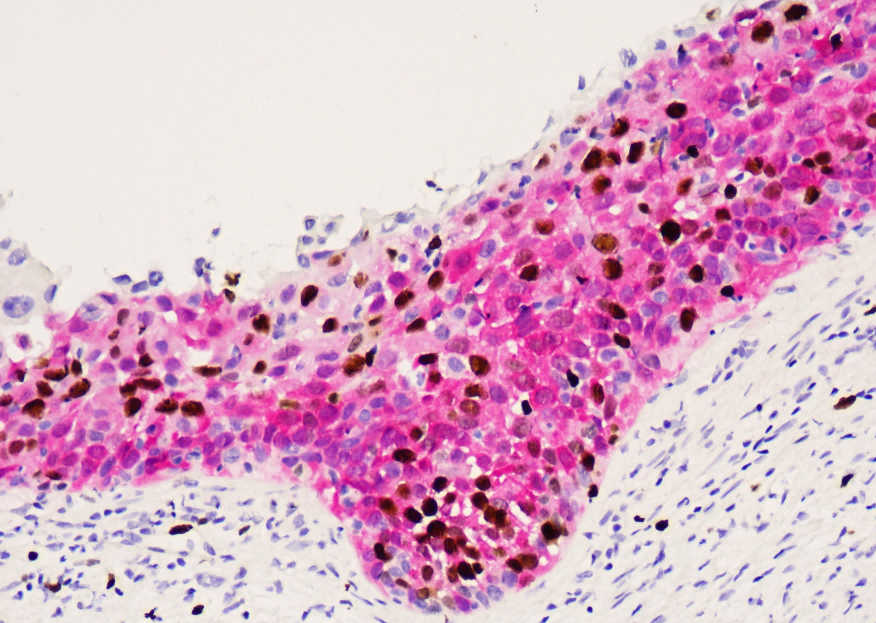
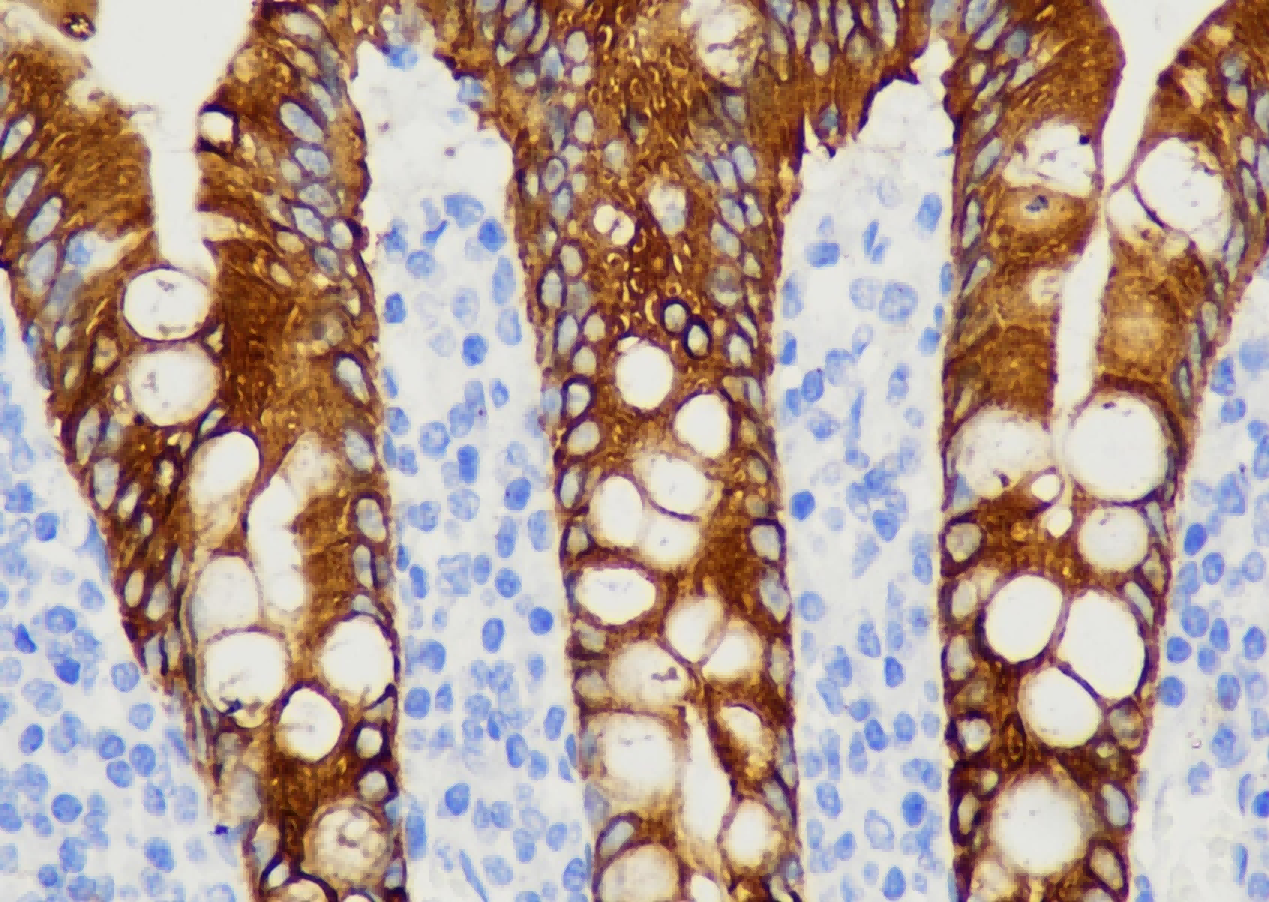
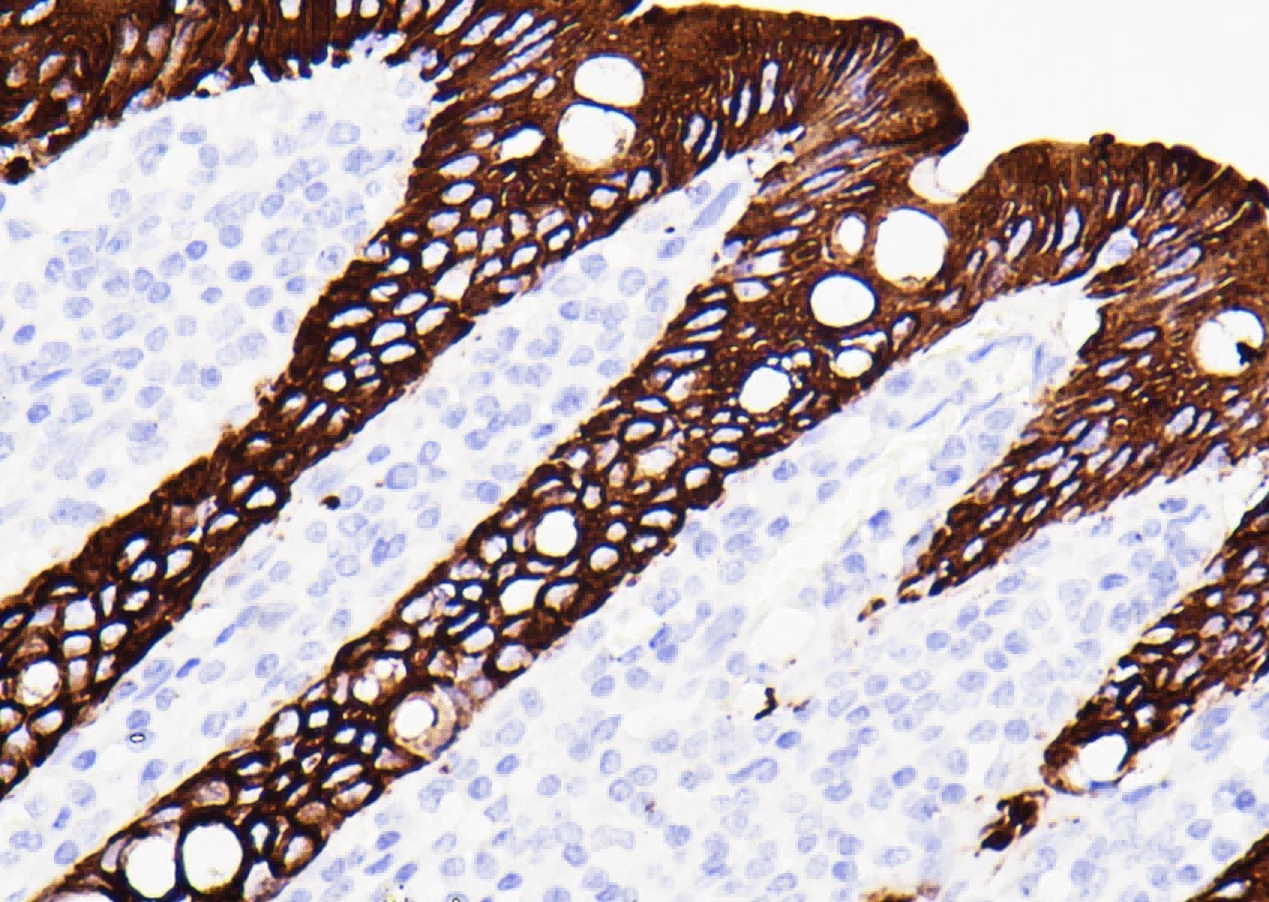
Common pathogenic fungi include Mucor, Aspergillus, Cryptococcus neoformans, Actinomycetes and Candida albicans.
The basic structural components of fungi contain a large number of mucopolysaccharides and proteins. These substances, after a proper amount of oxidants and a certain oxidation time, can cause the carbon bonds of ethylene glycol or aminohydroxyl groups in sugar structure molecules to break, generating aldehyde compounds, and then make the exposed free aldehyde groups combine with Schiff reagent and hexamine silver reagent, and then select the corresponding counterstain to enhance the contrast of tissue fiber components.